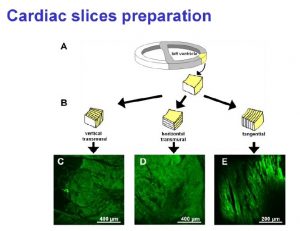
Multiple slice Recordings from Heart Slices
Heart Slice Model
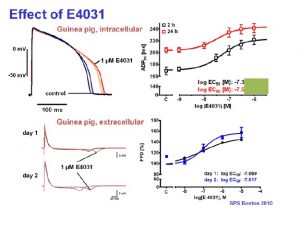
The long QT syndrome (LQTS) is characterized by the appearance of long QT intervals in the electrocardiogram. It is accomplished by atypical ventricular tachycardia like torsade de pointes and thus results in a high risk of sudden cardiac death. Therefore, the evaluation of a QT prolongation due to the action of new compounds plays an essential role in pharmacological development of new drugs and in safety pharmacology. Beside the common in vivo measurements of animal ECG and in vitro assays like the Langendorff heart model or the patch clamp analysis of herg channels expressed in mammalian cell lines the new technique of isolated living heart slices was developed during the last years. Our results demonstrate that standardized heart slices with normal physiology and pharmacology can be prepared from nearly any adult laboratory animal (mouse, rat, guinea pig, etc.) and even from human biopsy material.
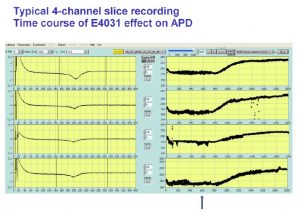
Physiological parameters including action potential duration (APD) can be measured over up to 30 hours with the Synchroslice multiple slice evaluation system in up to 4 heart slices simultaneously. Different test procedures can be performed including extracellular recording of stimulus induced cardiac field potentials or intracellular recordings from single cardiac myocytes. Many different parameters, e.g. action potentials duration, amplitude, latency, transmural differences, refractory periods, etc. are analyzed automatically.
Summary Heart slice method
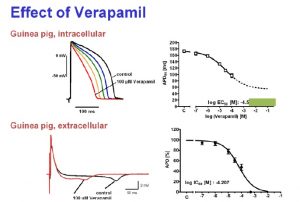
- Extracellular and intracellular recordings from cardiac slices correlate well with established in vivo and in vitro models in terms of pharmacology and predictability
- Cardiac slices are easy to handle and can be maintained over several days, allowing the reuse of the same preparations and the evaluations of long-lasting drug effects
- As many tissue slices can be prepared from one heart, the slice technique reduces the number of laboratory animals substantially
- Compared to other multi-cellular preparations cardiac slices offer the possibility of an enhanced throughput
References
- Bussek A, Wettwer E, Christ T, Lohmann H, Camelliti P, Ravens U: Tissue slices from adult mammalian hearts as a model for pharmacological drug testing. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 24(5-6), 527-536, 2009.
- Pugsley MK, Towart R, Authier S, Gallacher DJ, Curtis MJ: Innovation in safety pharmacology testing. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 64, 1-6, 2011.
- Himmel HM, Bussek A, Hoffmann M, Beckmann R, Lohmann H, Schmidt M, Wettwer E: Field and action potential recordings in heart slices: correlation with established in vitro and in vivo models. Br. J. Pharmacol. 166(1): 276-296, 2012
- Bussek A, Schmidt M, Bauriedl J, Ravens U, Wettwer E, Lohmann H: Cardiac tissue slices with prolonged survival for in vitro drug safety screening. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 66(2), 145-151, 2012.
Contact Us
You need more information? Just send us an email – we will get in contact with you as soon as possible